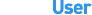
Выполнение правильной команды netstat в Windows 7 покажет все подключения, протоколы и порты и связанные программы, когда это возможно.
Netstat /?
Microsoft Windows [Version 6.1.7600]
Copyright (c) 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32>netstat /?
Displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections.
NETSTAT [-a] [-b] [-e] [-f] [-n] [-o] [-p proto] [-r] [-s] [-t] [interval]
-a Displays all connections and listening ports.
-b Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or
listening port. In some cases well-known executables host
multiple independent components, and in these cases the
sequence of components involved in creating the connection
or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable
name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called,
and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option
can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient
permissions.
-e Displays Ethernet statistics. This may be combined with the -s
option.
-f Displays Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN) for foreign
addresses.
-n Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
-o Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.
-p proto Shows connections for the protocol specified by proto; proto
may be any of: TCP, UDP, TCPv6, or UDPv6. If used with the -s
option to display per-protocol statistics, proto may be any of:
IP, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, TCP, TCPv6, UDP, or UDPv6.
-r Displays the routing table.
-s Displays per-protocol statistics. By default, statistics are
shown for IP, IPv6, ICMP, ICMPv6, TCP, TCPv6, UDP, and UDPv6;
the -p option may be used to specify a subset of the default.
-t Displays the current connection offload state.
interval Redisplays selected statistics, pausing interval seconds
between each display. Press CTRL+C to stop redisplaying
statistics. If omitted, netstat will print the current
configuration information once.