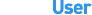
У меня есть машина с Ubuntu, и я хочу отправить поддельный IP-адрес (.212) на машину с Windows. Для этого я использую спуфинговую программу, которая использует необработанные сокеты.
192.168.1.185- IP моей машины (Ubuntu)192.168.1.212- поддельный IP (на самом деле это мой IPhone IP)192.168.1.213- Назначение (Мой планшет Windows)
Теперь, когда я передаю параметры (поддельный IP-адрес и пункт назначения) на выход программы, я никогда не вижу ни одного пакета с поддельного IP-адреса в пункт назначения в Wireshark. Все, что я вижу, - это пакет от неизвестного источника IP (64.17.17.214) к поддельному IP (.212). Я не могу понять, что происходит в Linux.
Использование команды: ./rawudp <source hostname/IP> <source port> <target hostname/IP> <target port>
Моя команда: ./a.out 192.168.1.212 80 192.168.1.213 8080
Вот скриншот: http://tinypic.com/r/ofrfb5/8
Вот программа: http://pastebin.com/cT4TBsKU
Исходный код напрямую:
// ----rawudp.c------
// Must be run by root lol! Just datagram, no payload/data
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/udp.h>
# include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// The packet length
#define PCKT_LEN 8192
// Can create separate header file (.h) for all headers' structure
// The IP header's structure
struct ipheader
{
unsigned char iph_ihl:5, iph_ver:4;
unsigned char iph_tos;
unsigned short int iph_len;
unsigned short int iph_ident;
unsigned char iph_flag;
unsigned short int iph_offset;
unsigned char iph_ttl;
unsigned char iph_protocol;
unsigned short int iph_chksum;
unsigned int iph_sourceip;
unsigned int iph_destip;
};
// UDP header's structure
struct udpheader
{
unsigned short int udph_srcport;
unsigned short int udph_destport;
unsigned short int udph_len;
unsigned short int udph_chksum;
};
// total udp header length: 8 bytes (=64 bits)
// Function for checksum calculation. From the RFC,
// the checksum algorithm is:
// "The checksum field is the 16 bit one's complement of the one's
// complement sum of all 16 bit words in the header. For purposes of
// computing the checksum, the value of the checksum field is zero."
unsigned short csum(unsigned short *buf, int nwords)
{ //
unsigned long sum;
for (sum = 0; nwords > 0; nwords--)
sum += *buf++;
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
return (unsigned short) (~sum);
}
// Source IP, source port, target IP, target port from the command line arguments
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int sd;
// No data/payload just datagram
char buffer[PCKT_LEN];
// Our own headers' structures
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *) buffer;
struct udpheader *udp = (struct udpheader *) (buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader));
// Source and destination addresses: IP and port
struct sockaddr_in sin, din;
int one = 1;
const int *val = &one;
memset(buffer, 0, PCKT_LEN);
if (argc != 5)
{
printf("- Invalid parameters!!!\n");
printf("- Usage %s <source hostname/IP> <source port> <target hostname/IP> <target port>\n", argv[0]);
exit(-1);
}
// Create a raw socket with UDP protocol
sd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_UDP);
if (sd < 0)
{
perror("socket() error");
// If something wrong just exit
exit(-1);
} else
printf("socket() - Using SOCK_RAW socket and UDP protocol is OK.\n");
// The source is redundant, may be used later if needed
// The address family
sin.sin_family = AF_INET;
din.sin_family = AF_INET;
// Port numbers
sin.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2]));
din.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[4]));
// IP addresses
sin.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]);
din.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[3]);
// Fabricate the IP header or we can use the
// standard header structures but assign our own values.
ip->iph_ihl = 5;
ip->iph_ver = 4;
ip->iph_tos = 16; // Low delay
ip->iph_len = sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct udpheader);
ip->iph_ident = htons(54321);
ip->iph_ttl = 64; // hops
ip->iph_protocol = 17; // UDP
// Source IP address, can use spoofed address here!!!
ip->iph_sourceip = inet_addr(argv[1]);
// The destination IP address
ip->iph_destip = inet_addr(argv[3]);
// Fabricate the UDP header. Source port number, redundant
udp->udph_srcport = htons(atoi(argv[2]));
// Destination port number
udp->udph_destport = htons(atoi(argv[4]));
udp->udph_len = htons(sizeof(struct udpheader));
// Calculate the checksum for integrity
ip->iph_chksum = csum((unsigned short *) buffer, sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct udpheader));
// Inform the kernel do not fill up the packet structure. we will build our own...
if (setsockopt(sd, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, val, sizeof(one)) < 0)
{
perror("setsockopt() error");
exit(-1);
} else
printf("setsockopt() is OK.\n");
// Send loop, send for every 2 second for 100 count
printf("Trying...\n");
printf("Using raw socket and UDP protocol\n");
printf("Using Source IP: %s port: %u, Target IP: %s port: %u.\n", argv[1], atoi(argv[2]), argv[3], atoi(argv[4]));
int count;
for (count = 1; count <= 20; count++)
{
// Verify
if (sendto(sd, buffer, ip->iph_len, 0, (struct sockaddr *) &sin, sizeof(sin)) < 0)
{
perror("sendto() error");
exit(-1);
} else
{
printf("Count #%u - sendto() is OK.\n", count);
sleep(2);
}
}
close(sd);
return 0;
}